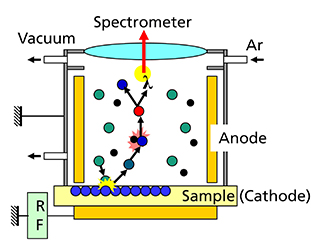
The determination of chemical depth profiles is of great importance for applications in the fields of optics, electronics, photovoltaics and battery technology. Glow discharge optical emission spectrometry is a very efficient method in terms of detection limits and depth resolution.
The combination of a radio frequency glow discharge with optical emission spectrometry (RF-GD-OES) enables the analysis of chemical depth profiles on both electrically conductive and non-conductive samples. For the analyses, the sample is sputtered as the cathode of an RF glow discharge on a spot diameter of 4 mm, atomic layer by atomic layer. Simultaneously, an excitation of the sputtered atoms takes place in the plasma of the glow discharge, which is associated with an emission of optical spectral lines of the chemical elements present in the sample. The intensity of the optical emission lines is then recorded for the different chemical elements with a spectrometer as a function of the sputtering time. By additional use of reference materials, quantitative concentration-depth profiles can be calculated from the measured qualitative intensity-sputtering time profiles of the emission lines.
The detection range of the concentrations reaches from 10 ppm to 100% for many elements. A depth resolution of a few nanometres is possible for smooth substrates. The intensity of the optical emission lines of 45 chemical elements including hydrogen can be registered simultaneously. By using a pulsed RF discharge, temperature-sensitive samples such as coated polymer films or coatings on glass substrates can also be analysed.
Typical applications at Fraunhofer FEP are the analysis of the chemical composition of oxide or nitride coatings for optical and electronic applications. Another important application is the analysis of impurities at the interface to the substrate, which have an influence on the adhesion strength of the coatings. GD-OES analyses are used on thin-film solar cells to determine concentration gradients which influence the absorption of sunlight. At the same time, doping profiles or possible impurities in the individual layers can be analysed. GD-OES analyses are also very interesting for battery applications, as the method can also be used to analyse lithium-containing layers.
GD-OES analyses are successfully used at Fraunhofer FEP in various projects to optimise our coating technologies and are also offered as an external service.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Electron Beam
Fraunhofer Institute for Electron Beam